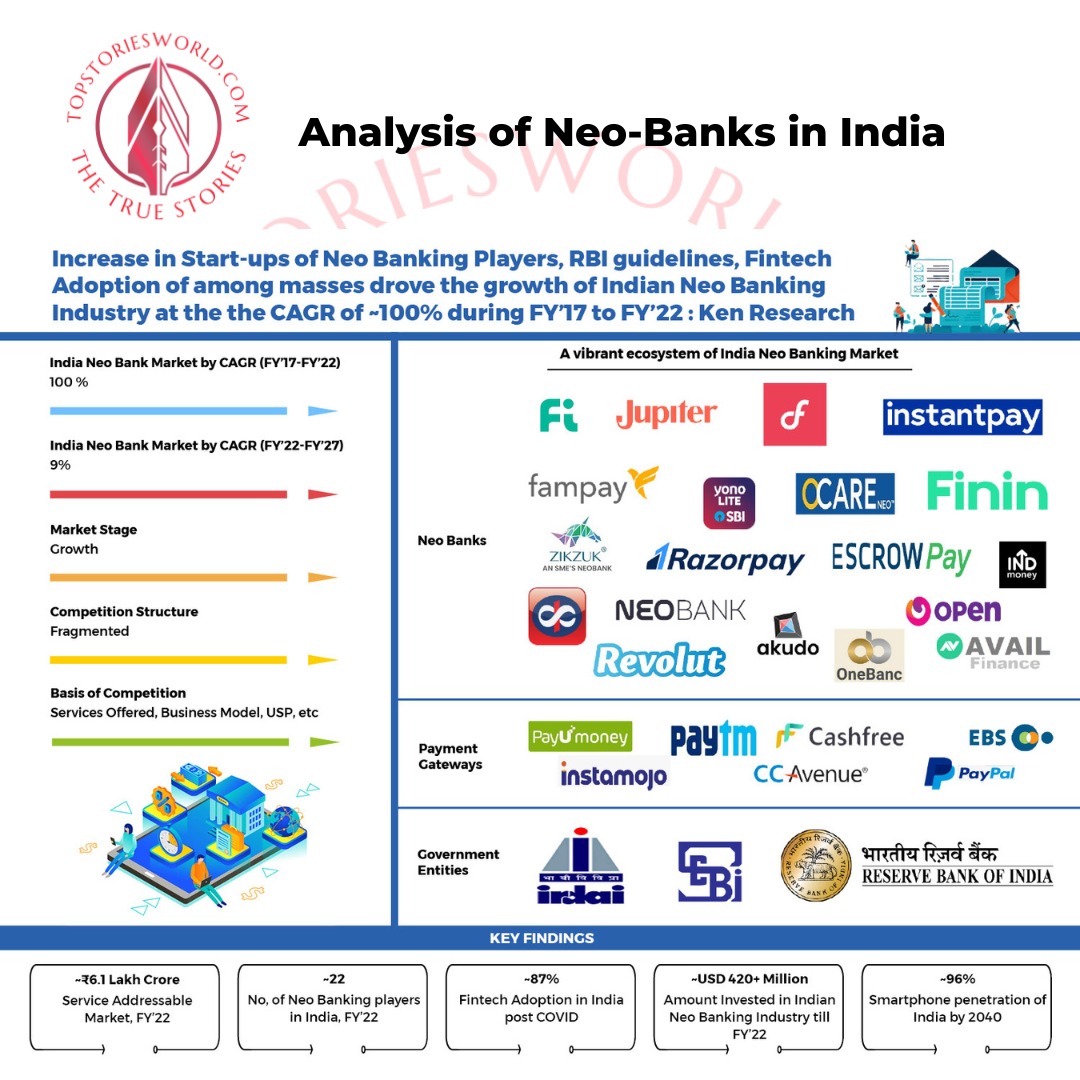
Breaking News
 But what sets neo-banks apart from traditional banks is their unique ability to disrupt the status quo. They are not restrained by legacy systems or complex regulations, allowing them to offer low-cost models and a customer-centric experience. This has made them popular among India's underserved Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSME) sectors.
But what sets neo-banks apart from traditional banks is their unique ability to disrupt the status quo. They are not restrained by legacy systems or complex regulations, allowing them to offer low-cost models and a customer-centric experience. This has made them popular among India's underserved Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSME) sectors.